 Last month, Ambry Genetics and Gene By Gene responded to Myriad's motion for preliminary injunction in a 109 page brief that sets out its invalidity case as well as the basis for its antitrust counterclaims. Supported by declarations from numerous luminaries and illuminaries in the gene patenting debate (including several of the individual plaintiffs in the Myriad case, and anti-gene patenting economist and Nobel Prize winner Joseph Stiglitz), the brief makes its points good and bad in an exhaustive fashion. Not surprisingly, the brief focuses on the Supreme Court's decision in the AMP v. Myriad Genetics case, categorical exclusion being the easiest and most direct for the defendants to prevail. The brief also alleges invalidity for anticipation or obviousness and non-infringement, as well as challenging Myriad's claims of irreparable harm, the balance of the hardships and the public interest, the latter based on the generic testing being "critical to patient care" (indeed, as in AMP, the intuitively persuasive argument is that patients will benefit, regardless of the evidence for or against that proposition).
Last month, Ambry Genetics and Gene By Gene responded to Myriad's motion for preliminary injunction in a 109 page brief that sets out its invalidity case as well as the basis for its antitrust counterclaims. Supported by declarations from numerous luminaries and illuminaries in the gene patenting debate (including several of the individual plaintiffs in the Myriad case, and anti-gene patenting economist and Nobel Prize winner Joseph Stiglitz), the brief makes its points good and bad in an exhaustive fashion. Not surprisingly, the brief focuses on the Supreme Court's decision in the AMP v. Myriad Genetics case, categorical exclusion being the easiest and most direct for the defendants to prevail. The brief also alleges invalidity for anticipation or obviousness and non-infringement, as well as challenging Myriad's claims of irreparable harm, the balance of the hardships and the public interest, the latter based on the generic testing being "critical to patient care" (indeed, as in AMP, the intuitively persuasive argument is that patients will benefit, regardless of the evidence for or against that proposition).
 The brief leads with its most compelling argument: that the Supreme Court's Myriad decision drew the patent eligibility line at whether a claimed DNA molecule had the same sequence as the molecule as it is found in nature, not whether the molecule was synthesized in the laboratory (the latter argument was persuasive to Judge Moore at the Federal Circuit). Less so is their reading of the applicability of the Court's Mayo decision, which defendants' argue invalidate Myriad's claims because the steps of amplifying and sequencing DNA was "well-understood, routine and conventional." While certainly not yet settled, Myriad's method claims are expressly outside the Supreme Court's Myriad decision and could fall within the scope of "applications" of the determination of the BRCA gene sequences the Court seemed to view with considerably more favor that the genomic DNA claims in the Myriad decision.
The brief leads with its most compelling argument: that the Supreme Court's Myriad decision drew the patent eligibility line at whether a claimed DNA molecule had the same sequence as the molecule as it is found in nature, not whether the molecule was synthesized in the laboratory (the latter argument was persuasive to Judge Moore at the Federal Circuit). Less so is their reading of the applicability of the Court's Mayo decision, which defendants' argue invalidate Myriad's claims because the steps of amplifying and sequencing DNA was "well-understood, routine and conventional." While certainly not yet settled, Myriad's method claims are expressly outside the Supreme Court's Myriad decision and could fall within the scope of "applications" of the determination of the BRCA gene sequences the Court seemed to view with considerably more favor that the genomic DNA claims in the Myriad decision.
The brief challenges Myriad even as to the statement of facts, in enumerated fashion and asserts its own Statement of Facts, supported by several declarations by putative experts. Many of these facts reconstruct the development of genetic diagnostic testing in the early 1990's, purporting that such testing was "widely used" and that the genetic variation in the BRCA genes was known prior to Myriad's patents (providing part of the factual bases for defendants' invalidity contentions). Additional facts include mapping studies that located the BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes to within 2-6 centiMorgans of chromosome-specific markers. (The speciousness of this argument is illustrated by the following graphic illustrating imperfectly the differences in scale between kilobases and centiMorgans):
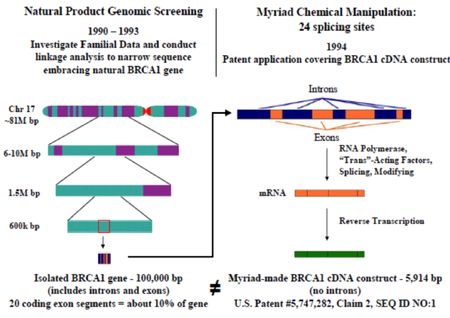 Interestingly, Gene By Gene's factual statement is framed in what the company "intends" to do, rather than is actually doing with regard to BRCA testing. The defendants also assert so-called "equitable" factual considerations regarding harm to them if enjoined, the fact that Myriad has not sued other putative providers, and that many patients "who want BRCA 1/2 testing cannot afford Myriad's BRCA 1/2 test price," and that Myriad's tests do not identify up to 10% of (rearrangement) mutations (begging the question of whether Myriad's asserted claims encompass such testing). And the brief cites San Francisco geneticist Robert Nussbaum regarding Myriad's proprietary genetic mutation database to support its argument that Myriad's frequency of variant of unknown significance cannot be verified.
Interestingly, Gene By Gene's factual statement is framed in what the company "intends" to do, rather than is actually doing with regard to BRCA testing. The defendants also assert so-called "equitable" factual considerations regarding harm to them if enjoined, the fact that Myriad has not sued other putative providers, and that many patients "who want BRCA 1/2 testing cannot afford Myriad's BRCA 1/2 test price," and that Myriad's tests do not identify up to 10% of (rearrangement) mutations (begging the question of whether Myriad's asserted claims encompass such testing). And the brief cites San Francisco geneticist Robert Nussbaum regarding Myriad's proprietary genetic mutation database to support its argument that Myriad's frequency of variant of unknown significance cannot be verified.
Defendants' legal arguments regarding Myriad's asserted composition of matter (probes and primer) claims start (and could end) with the Supreme Court's Myriad decision as the underpinnings of their argument that Myriad is not likely to prevail on the merits. Defendants' interpretation of the Supreme Court's Myriad decision (if correct, which it likely is) is dispositive:
If the DNA primer nucleotide sequence created in the lab corresponds to a natural DNA nucleotide sequence, then it is an unpatentable product of nature under Myriad.
Defendants cite portions of the specifications of the patents-in-suit as well as Myriad's arguments before the District Court, Federal Circuit, and Supreme Court to establish the distinction between natural and non-naturally occurring DNA, with genomic DNA and oligonucleotide primers in the former category and cDNA in the latter category. Under this analysis, the primers and probes recited in Myriad's asserted composition of matter claims fall within the scope of patent-ineligible subject matter according to the Supreme Court's Myriad decision. In this way, defendants argue that claims 29 and 30 of the '492 patent and claims 16 and 17 of the '282 patent are invalid as being directed to patent-ineligible subject matter (albeit based on one of the more strikingly inaccurate quotes from the Court's Myriad decision, no doubt being one of the factors that prompted Justice Scalia's concurrence). Unfortunately, the brief also reiterates the Court's misjudgment regarding the significance of the informational content of the primers as being dispositive, which might be compelling if the genetic information was itself either patent eligible or patented.
Turning to the method claims, defendants' arguments focus on the Court's Mayo v. Prometheus decision, in a manner that ignores portions of the Myriad decision that arguably distinguish Mayo from Myriad's asserted method claims. According to defendants, Myriad's method claims are patent-ineligible for reciting a law of nature using only "well-understood, routine and conventional methods," specifically PCR amplification and nucleotide sequencing. In defendants' view, they are merely an "artifice of patent drafting" (proving if nothing else that Supreme Court Justices should avoid dicta illustrating their prejudices more than illuminating the law), arguing that as dependent claims from method claims invalidated by the District Court and Federal Circuit (and not reviewed by the Supreme Court), these claims are also patent ineligible. Defendants analogize the BRCA genes with previously unknown laws of nature, which are then analyzed using "well-understood, routine and conventional" PCR and sequencing methods. Where this analysis falls apart, of course, is that the subject matter of the Mayo claims was in all aspects "well-understood, routine and conventional." Here, the "law of nature" is that some mutations are associated with disease and others are not; the distinction with the Mayo claims is that the isolated BRCA genes themselves were not in the prior art, in contrast with the step of administering 6-thioguanine to Crohn's disease patients. And there is no support for the proposition that, because the isolated BRCA genes themselves are not patent-eligible the method for determining a risk of disease by detecting certain mutations would not be. Importantly, the Supreme Court suggested that these types of claims may be patent eligible precisely because Myriad was the first to identify the BRCA genes:
[T]his case does not involve patents on new applications of knowledge about the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Judge Bryson aptly noted that, "[a]s the first party with knowledge of the [BRCA1 and BRCA2] sequences, Myriad was in an excellent position to claim applications of that knowledge. Many of its unchallenged claims [including the ones asserted in Myriad's complaint against Ambry and Gene By Gene] are limited to such applications."
It is also relevant that defendants attempt to bootstrap the District Court decision on claims arguably much broader and less specific than the now-asserted claims against Myriad, which would reward defendants for the AMP plaintiffs' strategic decision not to include these claims in its complaint.
Defendants also argue that Myriad's asserted composition of matter claims are invalid under §§ 102, 103 and/or 112. Regarding § 102, defendants first assert particular priority dates for specific claims based on the presence of specific disclosure in various applications in the priority chain of Myriad's asserted patents. Defendants then assert prior art, available at these several dates, in support of their anticipation arguments. None of this art discloses isolated human chromosomal DNA within the scope of the patent claims, i.e., that were sufficiently circumscribed in the vicinity of the BRCA genes that would have permitted the genes to be sequenced with the technology available in the 1992-1996 time frame. And indeed, the BRCA genes were not; ironically, one of the arguments asserted against Myriad in other contexts is that Myriad was not the first to isolate the BRCA 2 gene and that there is some question about its priority over Mary Claire King's lab regarding the BRCA 1 gene. However, because the asserted claims recite primers that amplify "all or a portion" of the BRCA 1 gene, some of these allegations are sufficiently specific regarding disclosure of primers for chromosome 17 markers that turned out to be portions of the BRCA genes that they may support a determination that Myriad has not shown a likelihood of success on the merits with regard to the assertion of these claims. In this regard, the arguments for the BRCA 1 claims are more likely to be persuasive than the arguments for the BRCA 2 claims, insofar as the primers for the chromosome 13 marker disclosed in the prior art are located entirely within an intron.
Defendants direct their obviousness attack under § 103 to Myriad's method claims. Here, the argument is that the amplifying and sequencing steps would have been obvious as a solution to the problem of identifying disease-associated BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 gene mutations. The obviousness of the BRCA genes is indicated by the knowledge in the art that there were genes on chromosomes 13 and 17 associated by genetic linkage analysis with a higher risk of developing ovarian and breast cancer, respectively. Finding the genes amounted to nothing more than "tedious, but straightforward [] mapping of human traits," according to plaintiffs. Most of this argument is precatory in nature "[h]aving stood on the shoulders of giants, Plaintiffs sought to claim the kingdom," and defendants reiterate their mantra of "using well-understood, routine and conventional" methods to isolate BRCA genomic DNA. This is not the test, however; indeed, the argument runs contrary to the express language of the statute, wherein "[p]atentability shall not be negatived by the manner in which an invention is made." The conventionality vel non of the methods would certainly be relevant for claims to methods of isolating BRCA gene DNA, but the methods themselves are irrelevant to the non-obviousness of the genes themselves. (It is amusing that defendants contend that "[t]he sizable investment by Plaintiffs' corporate partners and the federal government evidences (sic) Plaintiff's reasonable expectation of success in isolating the BRCA genes.") And In re Kubin is not to the contrary (despite defendants' argument), insofar as the facts in that case involved a next generation of cDNA (not genomic) cloning and had the benefit of specific antibodies to the gene product not present for the BRCA genes. Having asserted the obviousness of the genes themselves, defendants then assert that the methods claimed by Myriad would also have been obvious (again equated with the "well-understood, routine and conventional").
With regard to certain claims (including claim 5 of the '721 patent) defendants argue that the existence in the prior art of methods that detected variants in the BRCA1 gene not associated with disease renders obvious claims directed to variants that are associated with disease, "because it would have been obvious to identify additional polymorphisms." And Myriad's own '282 patent is cites as § 102(e) prior art in asserting some of these obviousness arguments. Whatever else can be said about this litigation, it is clear that Myriad's claims will get a full assessment of their patentability under the substantive portions of the patent statute.
Finally, defendants argue that certain of Myriad's asserted patent claims (including claim 7 of the '282 patent and claim 30 of the '492 patent) are invalid under § 112 for indefiniteness for being insolubly ambiguous with regard to amplification of exons and introns. Claim 4 of the '155 patent is asserted to be invalid for failure to satisfy the written description requirement (by reciting only variants that do not lead to an increase susceptibility for cancer).
Turning to non-infringement, defendants allege that Myriad has not "pinpointed specific evidence" to support infringement of its asserted composition of matter claims, characterizing Myriad's assertions as "speculations" regarding defendants' allegedly infringing activities. Defendants argue, for example, that the composition claim term that the primers are "derived from" or "isolated from" the human BRCA genes to mean "wholly derived from" (of "wholly isolated from") and thus the presence of heterologous sequences in Ambry's and Gene By Gene's primers place their methods outside the scope of literal infringement. Regarding the method claims, defendants argue that there is a similar lack of specificity regarding evidence of infringement. And insofar as Myriad's claims are directed to analyzing mRNA or cDNA (as in claim 8 of the '441 patent and claim 4 of the '857 patent), defendants argue that neither one of them determines BRCA gene sequences from that source, and in other instances (claim 5 of the '721 patent and claims 2 and 4 of the '155 patent) defendants argue that they don't "compare patient sequences to contiguous cDNA sequences." In their most interesting argument, defendants assert that they do not infringe because "they do not use or intend to use probes specific for any known variations of BRCA1 that predispose a patient to certain cancers," "[t]hat is, the probes that Ambry and Gene by Gene uses or will use will only identify BRCA1 and are not specific for any particular allele, as required by the claim."
In the final portion of the brief, defendants turn to the other requirements for obtaining a preliminary injunction: irreparable harm, the balance of the hardships tipping in favor of Myriad, and the public interest. The irreparable harm argument emphasizes Myriad's position as a "monopolist" and the amount of money Myriad has made (and cites Myriad's Dr. Skolnick's unfortunate interview with a POV journalist enshrined in the documentary film "In the Family"). Defendants also cite the institutional inertia attendant upon Myriad's agreements with insurance companies and other providers that are not capable of shifting providers quickly (although the price difference could certainly be expected to do so, and slow adoption has not been the case with other examples, such as generic replacement of patented drugs). Defendants emphasize the benefits their lower priced tests confer on patients, and the possibility of "meaningful second opinion testing" (emphasis in brief). Defendants challenge Myriad's assertion of the risk of "reputational" harm, and further argue that Myriad's "inconsistent" enforcement of its patents (Myriad allegedly is permitting "at least five other laboratories" to provide BRCA gene testing) mitigates against its allegations of "irreparable harm." The balance of the hardships, according to defendants is not with Myriad, due to its profits over the past 17 years, but with Ambry and Gene By Gene, who will lose the "first mover" advantage of their early entry into the market and Ambry's $46.7 million investment (an argument undercut by their earlier argument that "at least five other laboratories" are providing BRCA gene testing).
Defendants of course emphasize the public interest in this "life-saving technology":
This is precisely the kind of case where consideration of the public interest compels denial of injunctive relief. Indeed, courts have rejected injunctive relief on public interest grounds where removal of the accused product or process could have serious consequences on public heath -- even when the patentee has satisfied its burden as to the other factors. See, e.g., Hybritech, Inc. v. Abbott Labs., 849 F.2d 1446, 1458 (Fed. Cir. 1988).
This argument is followed by statistics on the number of women at risk of breast cancer and the number who are expected to die from the disease.
Somewhat curiously, defendants argue that the Court should deny the injunction because doctors and patients prefer their testing over Myriad's (despite their earlier contention that Gene By Gene is not yet offering the test). The basis for this "preference" is that Ambry and Gene By Gene will offer "multi-gene" testing, which defendants characterize as "comprehensive testing." In their final argument, defendants assert that Myriad does not offer "transparency, access and affordability" in its testing, which defendants will offer to the public's benefit.
Unfortunately, the brief ends with citations to arguments that Myriad's patents have harmed innovation because they have "blocked important follow on scientific research, hindered collaborative data collection and sharing, halted patient screenings at cancer diagnostic facilities, and prevented others from developing and/or offering additional, alternative, and more affordable technologies." The bases for at least some of these arguments are that Myriad enforced its patents against academic medicine that intended to charge its patients, activities clearly constituting infringement. And these assertions fly in the face of the more than 10,000 scientific research papers on the BRCA genes while Myriad's patents have been in force.
Myriad has replied, and that brief will be the subject of a future post.